Wall Footings
In that case of brick walls, the width of section are increased through 1/4 brick (5 cm) offset on either side. A base rests on a plain concrete footing that projects 10 to 15 cm beyond the last brick offset as display in Figure 7. The width at the base should not be less than the width of the supported wall plus 30 cm.
The depth of each course could be one brick or multiples of brick thicknesses. In the case of stone masonry walls, the offsets could be 15 cm along with the heights of the course as 30 cm. The depth of the concrete that is commonly of 1: 4: 8 (1 Cement: 4 Fine aggregate: 8 Coarse aggregate) or 1 : 5 : 10 : (1 Cement : 5 Fine aggregate : 10 Coarse aggregate) mix should not be less than 15 cm. From the wall the angular spread of load should not be more than 1 vertical to 1/2 horizontal within masonry and 1 vertical to 1 horizontal for cement concrete.
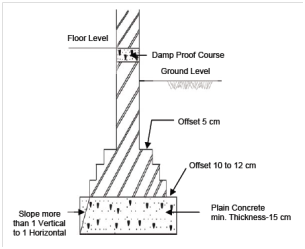
Figure 7: Wall Footing
If the load on the wall is heavy or the soil is of low bearing capacity and reinforced concrete strip footing could be given (Figure 8). The thickness of the strip could be decreased towards the edge to effect economy.
Figure 8: Strip Footing