Anthranilic acid:
Many compounds which form chelates with metal ions have been incorporated into resins while polycondensation with phenols and aldehydes. To cite an example, there is one with anthranilic acid. It is chosen for zinc and other transition metal ions.
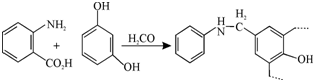
Other compounds that have been used are o- aminophenol, anthranilic acid- diacetic acid, m-phenylenediglycine.
There are chelating resins containing groupings similar to those of the more conventional chelating compounds, e.g., EDTA (ethylenediamine tetracetic acid) but attached to a cross linked matrix for gross insolubility. Those compounds strongly bond certain metal species which tend to form highly stable structures. Dowex A- 1, chelating resin, contains iminodiacetate groups attached to a cross linked polystyrene matrix.
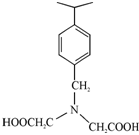
The resin has a very greater affinity for chelate forming di- and trivalent cations than for cations like Na+ or K+. This resin is particularly useful where one wishes to overcome the competing effect of high concentration of one or ions. Thus, it will effectively remove traces of heavy metal ions such as Fe3+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ from concentrated solutions of alkali and alkaline earth cations can be removed. Metals can be eluted from the resins with mineral acids. Selectivity among transition metal ions can be attained by adjustment of pH.