Cyclometer Mechanism:
The gear train is illustrated in given figure. C is a star wheel that is connected to the driving shaft. This is operated through a striker fixed to the wheel of the bike and makes 1/5 th of a revolution for one revolution of the wheel. There are two co-axial internal gears S and R from which R is fixed. The gear Q meshes along S and P meshes along R. The internal gear S makes one revolution for 1 km travelled by the bike.
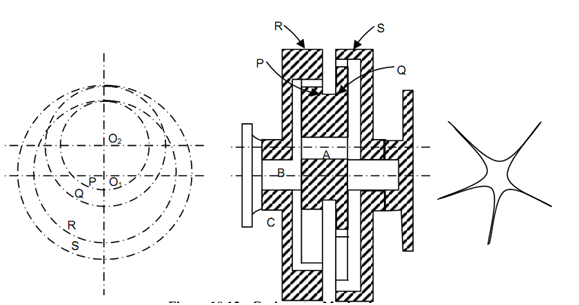
Cyclometer Mechanism
The gear train is illustrated in figure. The reason of the rear-axle differential is to allow the two side wheels to rotate at different speeds while automobile takes a turn. It could be possible due to the reason two degrees of freedom of the epicyclic gear train. Gears A and B constitute last drive and provide fixed gear ratio in the vehicle. Gears E and D have equivalent number of teeth and they are keyed to two partition of rear axle. These two portions of axle are linked to the two side wheels. While automobile moves along a straight road, there is no relative motion among pinion C and gears D and E. The planetory pinions behaves like keys to transmit motion through ring gear B to the gears D and E and so wheels rotate at similar speed. At what time vehicle takes a turn, the planet gear C begins rotating around their axis and two side gears D and E rotate at different speeds having one input speed. But, the average of speeds of D and E remains same to input speed.