Reverse Osmosis (RO):
The Reverse Osmosis (RO) is a process wherein a relatively pure solvent is separated from a salt solution by using a semipermeable membrane by the application of hydrostatic pressure. The hydrostatic pressure can vary from 2 MPa to around 6 MPa depending upon the salt content of the feed mixture. The solvent permeates preferentially by the membranes while the solutes, particularly electrolytes and low molecular weight nonelectrolytes are retained through the membranes. For efficiently retaining microsolutes having molecular weight less than 300 or effectual size less than 10 Å , reverse osmosis process is used. The process is used to produce relatively pure water or a concentrated solution of microsolutes from a given salt solution.
A simple schematic of the process is given in Figure. The most notable instance of reverse osmosis procedures is the production of drinking water from naturally occurring saline waters. This procedure is discussed in more detail in following sections of this unit.
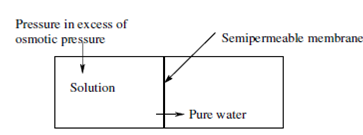
Figure: The schematic representation of a reverse osmosis process