Risk Projection
Risk projection which is also called risk estimation is attempts to rate each risk in 2 ways the probability or likelihood in which the risk is real and the consequences of the problems related with the risk should it occur. The project planner along with other technical and managers staff, performs 4 risk projection activities that are as follows
(1) Establish a scale which reflects the perceived likelihood if a risk.
(2) Delineate the consequences of the risk.
(3) Estimate and impact of the risk on the project and the product and
(4) The overall accuracy of the risk projection by that there will be no misunderstandings.
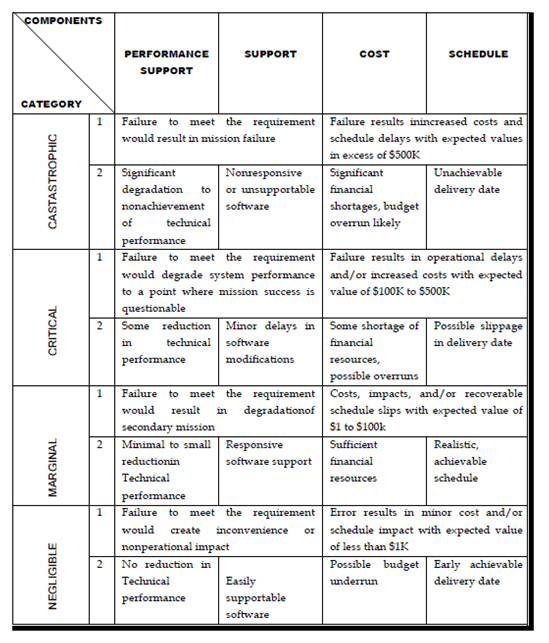
Figure - Impact assessments (BOE89)
There is a project team starts through listing all risks no matter how remote in the first column of the table. Each risk is differentiation in the 2nd column for example implies a project size risk BU implies a business risk. Probability of occurrence of each risk is entered in the next column of the table. The probability value for each risk can be estimated through team members individually. By the individual values are averaged to established a single consensus probability after that next the impact of each risk is assessed. Each and every risk component is assessed using the characterization presented in and an impact category is determined. The categories for each of the 4 risk parts support, performance, cost, schedule and are averaged to overall impact value and determine impact value.
1. Catastrophic 2. Critical 3. - Marginal 4. - Negligible
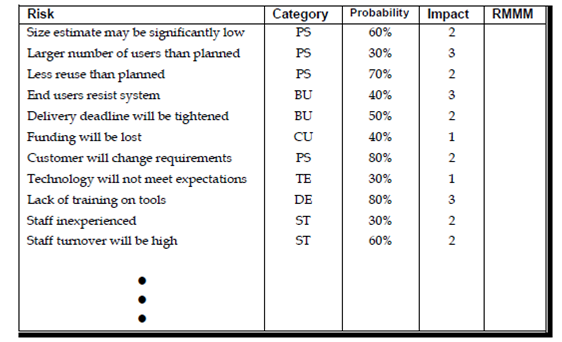
Figure -Sample risk table prior to sorting
Once the first 4 columns if the risk table have been completed then the table is sorted through probability and through impact. High-probability and high impact risks percolate to the top of the table and low probability risks drop to the down. This accomplished first order risk prioritization.
Project manager defines a cut off line and studies the resultant sorted table. The cut off line drawn horizontally at some point in the table implies which are only risks that lie above the line will be given further attention. The risks that fall below the line are reevaluated to accomplish 2nd order prioritization. Risk probability and impact have a distinct influence on management concern. A risk factor which has a high impact but a very low probability of occurrence should not absorb a significant amount of management time. Weather, low impact risk with high probability should be carried forwarded into the management steps and high impact risk with moderate to high probability that follow
All risks which lie above the cut off line must be managed. The column labeled RMMM carry a pointer in a Risk Monitoring, Management Plan and Mitigation established for all risk which lie above cut off.
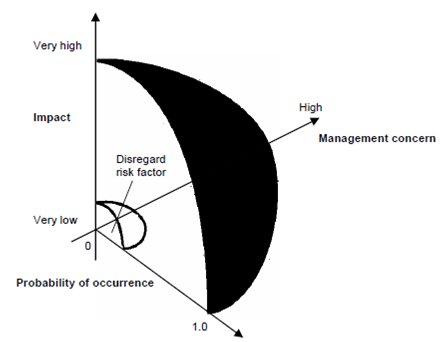
Figure - risk and management concern
The Risk probability can be determined through making individual estimates and then established a single consensus value. Whereas that approach is workable, more sophisticated method for determining risk probability has been build. The Risk drivers can be assessed on a qualitative probability scale which has the various values, improbable, impossible, probable, and frequent. The Mathematical probability can then be related with each qualitative value for example probability of 0.7 to 1.0 implies a highly probable risk.