Change Control
For a huge software development project uncontrolled change rapidly leads to chaos. Modification Control combines human process and automated tools to give a mechanism for the control of change. The change control procedure is describing schematically in figure a change request is evaluated and submitted to assess technical merit potential side effects overall impact on other and system functions the projected cost and configuration objects of the modification. The results of the evaluation are presented as a change report that is used by a change control authority (CCA) a person or group who makes a final decision on the status and priority of the modify. An engineering change order ECO is generated for each approved change. The ECO define the change to be made the constraints which must be respected and the criteria for audit and review the object to be modified is checked out of the project database the modification is appropriate SQA activities made and applied. The object is then checked in to the appropriate and database edition control mechanism is used to build the next edition of the software.
The Check in and Checkout procedure implement 2 important factors of modification control synchronization control and access control. The access control governs that the software engineers have the authority to modify and access a particular configuration object. The synchronization control helps to ensure which parallel modification performed through 2 different people do not overwrite one another [HAR89].
Need for change is recognized Change request from user Developer evaluates
Synchronization and Access control flow is described based on approved ECO and change request a software engineer checks out a configuration object. By an access control function ensures in which the software engineer has authority to check out the object and synchronization control locks the object in the project database so with this no updates can be made to it until the edition currently checked out has been exchange. Note that other copies can be checked out but other updates cannot be made. A copy of the baseline object is called the extracted version is change through the software engineer. After appropriate testing and SQA the new baseline object is unlocked and the change version of the object is checked in.
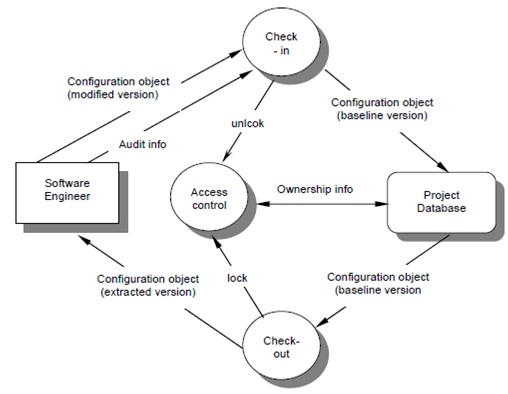
Figure - Access and synchronization control
In the world some readers may start to feel uncomfortable with the stages of bureaucracy implied through the change control procedure description. This feeling is not uncommon. Without proper safeguards changed control can create unnecessary red tape and retard progress. Many software developers who have modified control mechanisms have build a number of layers of control to help avoid the problem alluded to above.
To prior an SCI becoming a baseline only informal change control required to be applied. The developer of the configuration object (SCI) in question may make whatever changes are justified through technical requirements and project as long as modify do not impact broader system needs which lie outside the developer's scope of work. Once the entity has undergone formal technical review and had been approved a baseline is build. Once an SCI becomes a baseline project level modify control is implemented. At present to make a modification the developer must gain approval from the project manager if the change is local or form the CCA if the change impacts other SCIs. In some cases normal generation of modification requests change reports and ECOs is dispensed with. Moreover assessment of each modification is conducted and all changes are reviewed and tracked.
When the software product is publish to customers formal modification control is described. The formal modification control process has been described in figure.
The (CCA) change control authority plays an active role in the 2nd and 3rd layer of control. It is depend on the size and character of a software project the CCA may be comprised of one person - the project manager - or a number of people example for representatives from hardware, marketing, software, database support, engineering, etc. The primary role of the CCA is to take a worldwide view which is assessing the impact of change further the SCI in question like how wills the change affect hardware? And how will the change affect performance? How will the change modify the customer's perception of the product? How will the change affect product reliability and quality? These are the basic questions which are addressed through the CCA.