Theory of Second Best:
Government takes steps to make this market competitive, it would appear that social welfare would increase (as price and marginal cost will be equated in this market) irrespective of whether in some other markets competition cannot be enforced and therefore in them Pareto optimality conditions cannot be satisfied. The second best theory holds that, this will not lead to the increase in social welfare. In other words, the second best solution is not desirable. Although a fonnal proof of the theory of second best is bit complicated, it can be represented graphically in the Figure below.
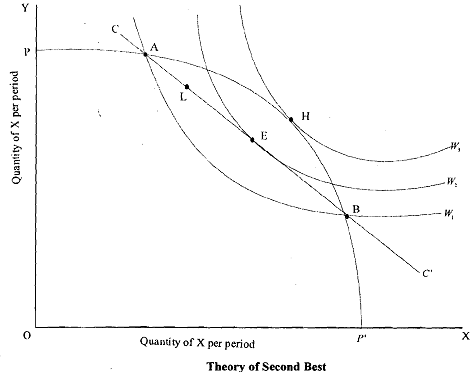
In the Figure, PP' is the production possibility curve and all points on the curve are Pareto efficient. According to Lipsey and Lancaster, it is sometimes better to move inside PP' to achieve a higher level of social welfare in case all marginal conditions are not satisfied. To demonstrate this, social welfare curves or community indifference curves are drawn in the figure like individual indifference curves. These social welfare curves represent combinations of two products X and Y, which yield the same level of social welfare. Further, the higher the level of social welfare curve denotes higher level of welfare. It will be seen from the figure that point Hat which social welfare curve is tangent to PP' shows maximum social welfare point satisfying all the marginal conditions of Pareto optimality. Now, suppose due to the existence of monopoly in the markets of the two goods, X and Y, the socially best point H is unattainable. Further, suppose that under such circumstances, combinations lying on the line CC' are attainable. Suppose the economy is at present at point L on the attainable line CC'. If Pareto optimality is to be achieved, we can move from a point L, which is inside PP' to point A or B which are also on the attainable line CC'. However, as will be seen from the figure, moving to point A or B on PP' would put us in a lower welfare curve W1 If instead from point L, we move the point E, which is inside PP' and is therefore Pareto inefficient and yields a higher level of welfare as indicated by Wz. Thus, the theory of second best asserts that when one of the marginal conditions of Pareto optimality is not satisfied due tosome or other reasons, it may be better to violate other marginal conditions of Pareto optimality to achieve maximum possible social welfare.
The theory of second best has been applied to question, the desirability of advocating competitive pricing in some particular markets when it is known that Pareto conditions do not hold in other markets. However, the advocates of such policies in making some markets more competitive in achieving Pareto optimality argue that as the markets in question are unrelated, it does not matter for attaining maximum social welfare that in other market conditions for Pareto efficiency are not fulfilled. Advocates of the latter policy argue that when markets are relatively independent or unrelated, marginal cost pricing increase social welfare. Thus, in the words of Prof. S. Charles Maurice and Own. R. Phillips, "the theoy of second best applies most strongly when
markets are closely related: that is, they either produce cornplementa y goods like bread and butter, or one market is an intermediate supplier of another as in the case of tyre makers supplying automobile producers".