Social Welfare Function and the Social Optimum:
Treating a number of economic variables as inputs, a social welfare function gives a measure of the aggregate material welfare of a society. Abram Bergson first introduced the idea of a social welfare function in his article 'A Reformulation of Certain Aspects of Welfare Economics' in 1938. By introducing the concept of 'social welfare function', Bergson and Samuelson approached welfare analysis in a different way. They based the concept of SWF on ordinal preferences of individuals and argued that welfare economics is essentially a normative study, but the approach should be scientific despite the fact that the incorporation of value judgments in it is simply unavoidable.
It would be prudent to have a brief overview of some alternative welfare functions, which will be helpful in bringing out some embedded ethical judgments. The classical welfare function was put forward by Bentham, Pigou and Marshall, popularly known as 'Benthamite welfae function'. According to them, social welfare is the sum of cardinal utilities obtained by all members
of a society. In algebraic form, this can be denoted as:
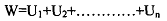
where W denotes social welfare, UI, Ub etc; represent the cardinal utilities of the individual members of the society. The goal of a society is to maximise social welfare, that is, the aggregate of the utilities of the individual members of society. Given this, maximum social welfare will be achieved if income is so distributed that marginal utility of income is equal for all individuals in a
society. Moreover, the classical viewpoint is that maximisation of social welfare is achieved only with equal distribution of income.
Another important social welfare function has been propounded by the noted philosopher John Rawls. Rawls analysed welfare economics by posing a problem: "what type of welfare criterion would be adopted by the society when it is in such an initial position where everybody has to behave under uncertainty about how the welfare criterion chosen will ultimately aflect his utility or welfae". Assuming that individuals are risk averse, he asserts that such a welfare criterion will be chosen that deviations from perfect equality would be made only when with unequal distribution of utilities, the worst oSf individual is better off actually than under equality conditions. This can be stated algebraically as follows:
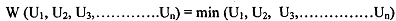
This implies that social welfare of resource allocation depends only on the worst off individual, that is, the person with minimum utility. Social welfare fhnction is an ordinal index of society's welfare and is a function of the utility level of all individuals comprising the society. The "Bergson-Samuelson" social welfare fhnction (SWF) can be expressed in the following general form:
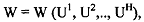
where "society's" welfare denoted by W, is merely a hnction of the utilities of its constituent members, uh, h = 1, 2, ........ H, where H are the number of households in the society. In other words, u', u2,.., uH represents the ordinal utility indices of different individuals or households in the society. The ordinal utility index of an individual depends upon the goods and services she consumes and the magnitude and kind of work she does and the amount of leisure she enjoys.
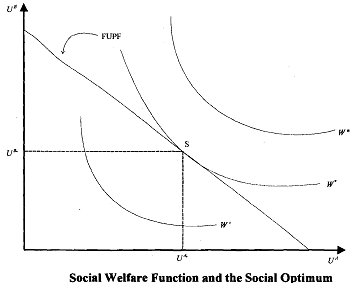
The Bergson-Samuelson SWF can be explained with the help of the grand utility possibilities frontier (GUPF). We know that every point on the GUPF is a Pareto-optimal allocation, and thus it seems that no point is necessarily preferable to another. The Bergson-Samuelson SWF shows that, given the set of Pareto-optimal points, which is' more desirable from "society's" point of view, where the notion of social desirability was subsumed in a social welfare function.