Rawlsian Welfare Function:
Thus, social welfare is a hnction of the levels of utility of members in the society. Alternatively, the social welfare function can be expressed as a function of other variables relevant to welfare, such as income or life expectancy. The form of the social welfare function can be seen as expressing a statement of the objectives of a society. For example, take a social welfare function:
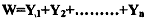
where W is social welfare and Y, is the income of each of the Xth individual in a society. In this case, maximising the social welfare function means maximising the total income of the people in the society, without regard to how incomes are ,distributed in the society. Alternatively, consider the Max- Min utility function:
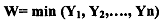
Here, the social welfare of the society is taken to be related to the income of the poorest person in the society, and maximising welfare would mean maximising the income of the poorest person without regard for the incomes of the others.
These two social welfare functions express very different views about how a society would need to be organised in order to maximise welfare. While the first emphasises the total incomes, the second considers the needs of the poorest.
However, often choice of such a function is considered part of political economy. Choosing between two such functions may be a matter of tolerances versus preferences, or some broader political or ethical issue that cannot be resolved by economics at all. A related problta is the need of individual capital for rest and recreation, which prevents anyone from actually maximising the total income. This is at the root of many of the balanced growth assumptions of macroeconomics: Unless a uniform social welfare function is chosen across an entire society, growth is not balanced. Due in part to this concern, more direct means of measuring well-being than "total incomes" or GDP are required by modem human development theory. Amartya Sen makes the point more directly: "What is the relation between our wealth, and our ability to live as we would like?" Without answering this question, income and welfare are only indirectly related.