Drying
The reason of sludge drying is to decrease the water content to less than 10% through evaporation, making the sludge suitable for incineration or processing within fertilizer. Drying is performed mechanically through the application of auxiliary heat. Mechanical processes used for this reasons are described briefly below and illustrated in Figure 5.
Flash Dryer
Sludge is pulverized within a cage mill or through means of atomized suspension methods in the presence of hot air.
Spray Dryer
Liquid sludge is fed into a high-speed centrifuge bowl. Centrifugal forces atomize the sludge within fine particles and spray them into the top of a drying chamber.
Rotary Dryer
Includes direct or indirect heating. Direct-heat dryers bring the sludge into physical contact along with hot gases, while in indirect-heat dryers; the central cell containing the sludge material is surrounded with steam.
Multiple-Hearth Dryer
Heated air and products of combustion are passed over finely pulverized sludge which is raked continuously to expose fresh surfaces.
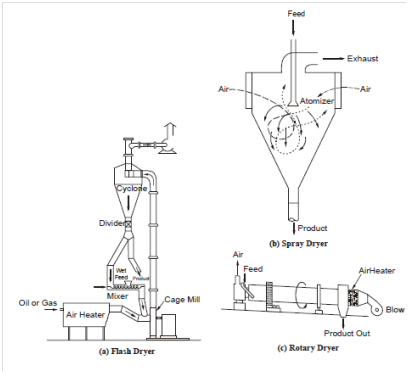
Figure 5: Sludge Dryer Technologies