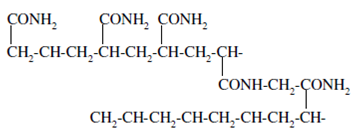SDS-PAGE Gel Electrohpresis:
In this method, protein samples are run by page-gel along with the help of a potential and differential mobility of various protein samples is responsible for their separation according to the mass of the protein. Polyacrylamide gels are created from the polymerization of two compounds viz. acrylamide and N, N-methylene- bis- acrylamide. Bis acrylamide is a cross-linking agent for the gels. The polymerization is initiated through the addition of ammonium persulphate along along with either -dimethylamino-propionitrile (DMAP) or N,N,N,N,- tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED).
Gels are caste in among two glass-plates and combs are also used to prepare the wells. Such as DNA-gel casting, combs are erased after polymerisation of the polymer. The gels are neutral, hydrophillic, three-dimensional networks of long hydrocarbons crosslinked through methylene groups. Acrylamide (CH2=CH-CO-NH2) and methylenebisacrylamide (CH2=CH-CO-NH-)2CH2 react in presence of ammonium persulphate (APS), (NH4)2S2O8. The APS is the sulphate free radical generator and crossed connected polymeric slab is produced.