Structural form and reduced form:
We presented the simultaneous equation. These equations are known as the 'structural equations' or 'behavioral equations' as they represent the structure (of an economic model) or the behavior of an economic agent (e.g., consumer or producer). The β and y' in are known as the structural parameters or coefficients. Recall that in the structural equations both endogenous and exogenous variables are on the right-hand side of each equation.
By solving for the M endogenous variables from the structural equations we can derive the reduced-form equations and the associated reduced-form coefficients. A reduced-form equation is one where each equation contains one endogenous variable and that endogenous variable is expressed solely in terms of the predetermined variables and the stochastic disturbances. To illustrate, let us consider the Keynesian model of income determination given at example.
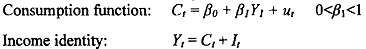
In this model C (consumption) and Y (income) are the endogenous variables and I (investment expenditure) is treated as an exogenous variable. While the first equation is stochastic in nature the second one is an identity. As usual, the MPC (β1) is assumed to remain between 0 and 1.
We obtain after simple algebraic manupulation
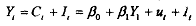
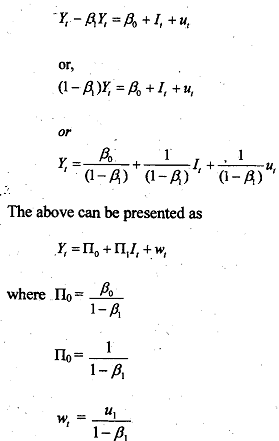
Equation is a reduced-form equation. It expresses the endogenous variable Y solely as a function of the exogenous (or predetermined) variable and the stochastic disturbance term. no and n, are the associated reduced- form coefficients. Notice that these reduced-form coefficients are nonlinear chmbinations of the structural coefficients(s).
Substituting the value of fiom (13.26) into C, of (1 3.24), we obtain another , reduced-form equation:
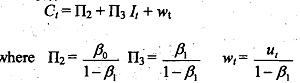
In the context of econometric models, equations such as (13.25) or Qdt = Qst( (Quantity demanded equal to quantity supplied) are known as the equilibrium condition. Identity states that aggregate income Y must be equal to aggregate expenditure (i.e., consumption expenditure plus investment expenditureb When equilibrium is achieved, the endogenous variables assume their equilibrium values.