Deformation of Bars
Bars of Uniform Section
Along the knowledge gained already, you shall now be able to study calculation of deformations in solids because of applications of simple stresses. Let us begin with the example of a prismatic bar having length 'L', uniform cross section of area A carrying an axial load 'P' as illustrated in specified in Figure.
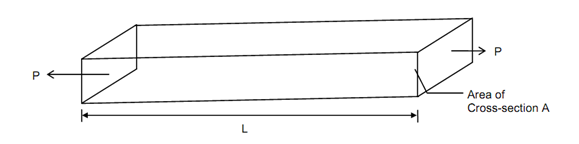
In the solid, Stress is in the longitudinal direction & its magnitude might be determined as
σ = Load / Area = P/ A
If the Young's Modulus of the material, E, is known, the strain induced might be determined as
ε = σ / E = P /AE
As only strain is deformation per unit length, the entire elongation of the bar is determined as
δ = ε. L = (P / AE) L
Therefore,
Elongation δ = PL/ AE
You might please note that the strain, ε, determined here is in the longitudinal direction and is accompanied by strains in the lateral directions also whose magnitude is specified by - υε. Now let us consider a few numerical instances.