G protein-coupled receptors
The GPCRs (G protein-coupled receptors) form a very big collection of cell surface receptors which are coupled to signal-transducing trimeric G proteins. Overall GPCRs hold seven membrane-spanning α-helical regions with their N-terminus on the extracellular face of the plasma membrane and their C-terminus on the cytoplasmic face. The GPCR family involves receptors for numerous hormones and neurotransmitters, light-activated receptors (rhodopsins) in the eye and thousands of odorant receptors in the mammalian nose. On the binding its ligand, a GPCR activates the signal-transducing trimeric G proteins guanyl nucleotide (GTP)-binding proteins that in turn activate or inhibit an effector protein. Trimeric G proteins consist of three subunits that are: α, β or γ. The Gα subunit is a GTPase trigger protein which alternates among an active (on) state
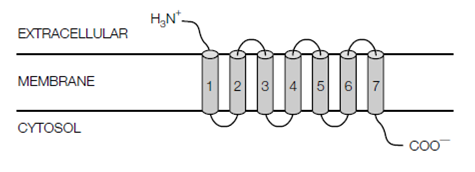
Figure:G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) contain seven transmembrane -helical regions (cylinders 1-7), with their N-terminus on the extracellular side of the membrane and their C- terminus in the cytosol.
and an inactive off state. In humans genome there are several copies of every of the α, β or γ subunits, giving diversity in the signaling by GPCRs.
The Gα and Gγ subunits are connected to the cytosolic surface of the plasma membrane through covalently connected lipids. In the resting state when no ligand is bound to the GPCR the Gα subunit is connect to GDP and hard by Gβγ. Binding of the ligand to the GPCR modifies its conformation causing it to bind to the Gα subunit in like a way which the GDP is displaced and GTP becomes bound. The Gα subunit then dissociates by Gβγ but both remain anchored to the membrane. The Gα subunit with GTP bound then interacts with and activates an related effector protein, like as adenylyl cyclase, or in some cases regulates the opening of an ion channel causing a modifies in the membrane potential. Moreover, this activation is short-lived, as the GTP is quickly within seconds, hydrolyzed to GDP through the intrinsic GTPase activity in the Gα subunit. The Gα subunit, now with GDP bound dissociates from the effector protein and deactivating it, and reassociates with Gβγ and ready for another round of activation and nucleotide replace in the given figure.
The hormone epinephrine binds to several different GPCRs. On binding to - adrenergic receptors on the surface of adipose and liver cells, epinephrine promotes glycogenolysis and lipolysis, in that order. On
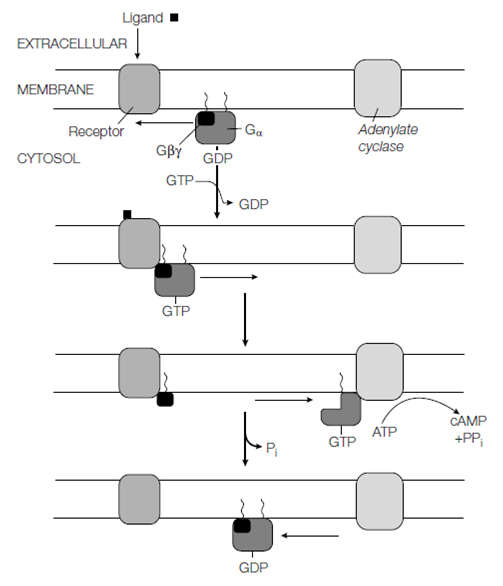
Figure: Signal transduction through a G protein-coupled receptor (see text for details).
smooth muscle cells lining the blood vessels in the skin, kidneys, and intestine epinephrine binds to the 2-adrenergic receptor causing the arteries to constrict. β-adrenergic receptors are coupled to the stimulatory G protein (Gs) which activates the membrane-bound adenylyl cyclase, while the α1-adrenergic receptor is coupled to an inhibitory G protein (Gi) which inhibits adenylyl cyclase, although the Gq protein coupled to the α2-adrenergic receptor activates a various effector protein. Therefore by binding to various receptors and activating several G proteins one ligand can switch a variety of various actions in various target cells.