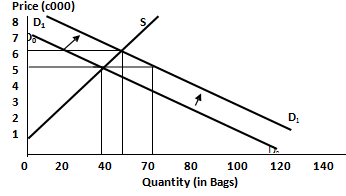
Change in Demand:
A change in demand as already noted completely shifts the demand curve either to the right when it is an increase in demand or left when it is a decrease in demand. A change in demand with supply remaining unchanged will affect both the equilibrium price and quantity and this is what is referred to as the partial equilibrium analysis.
Increase in Demand
An increase in demand shifts the demand curve to the right and when supply conditions remain unchanged then the equilibrium price will increase and the equilibrium quantity will also increase. Figure illustrate this. An increase in the demand for Amala while supply remains the same will shift the demand curve from DOD0 to D1D1. At the original market equilibrium rice of c5,000, there will be excess demand or shortage of about 30 (70 minus 40) bags which will in turn cause the market equilibrium price to rise to c6,000 and the equilibrium quantity to increase to 50 bags.