Calculating Shearing Stress:
As per perpendicular axis theorem,
Izz = Ixx + Iyy
From a circular section,
I xx = I yy = (π /64 )d 4
where d is refer to the diameter of the circular shaft.
Hence, J = I zz = πd 4 / 32
The term J / (d /2) is known as torsional section modulus or polar modulus, mention by Zp. It is same to section modulus, Z, which is equal to M/l.
Therefore, polar modulus for a solid shaft
Z p = πd 4/32 .2 /d = πd 3 /16
A hollow circular section is just like a circular section with only difference in the value of J. J for a hollow section can be calculated as different of J values of sections of outer diameter (d0) and inner diameter (di).
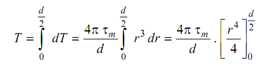
where respectively d0 & di are the outer and inner diameters.
Eq. may be compared with equation of bending M/I = σ/ y = E / R.
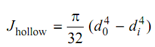
The expression τr /r corresponds to σ/y , T /y corresponds to M/I and Gθ /l corresponds to E . The expression GJ corresponds to expression EI.
The term GJ is called as torsional rigidity and the term EI is called flexural rigidity.
It can be noted that:
(a) T / θ, i.e. torque needed for unit twist, is called as the torsional stiffness of the shaft.
(b) T / (θ/ l), that means torque divided by the angle of twist per unit length, is called the torsional rigidity.
Units of various quantities mentioned above are usual. T is normally measured in Nm, τr, τm and G have units of N/m2 (Pa) or N/mm2, l is measured in m. θ contains radians as units.