Forward Breakover:
It takes a certain minimum voltage for conduction to take place whenever a p-n junction is related in such a manner which is shown by figure below. This minimum voltage is known as the forward breakover voltage (or merely the forward breakover) for the diode. Depending on the kind of material from which a diode is produced, the forward breakover voltage can variety from around 0.3 V to around 1 V. When the voltage across the p-n junction is not at least as great as the forward breakover, the diode will not conduct significantly.
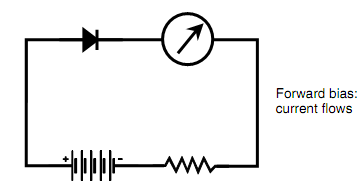
Figure: Forward bias of a diode results in a flow of current
The Forward breakover voltages of multiple diodes add altogether as when the diodes were batteries. Whenever two or more diodes are connected in series with their p-n junctions all oriented in a similar way, the forward breakover voltage of the combination is equivalent to the sum of the forward breakover voltages of each diode. Whenever two or more diodes are connected in parallel with their p-n junctions all oriented in similar way, the forward breakover voltage of the combination is similar as that of the diode whose forward breakover voltage is the smallest. The p-n junction is exclusive in this respect. It does not conduct absolutely in the forward direction, though it does not act quite such as a dc resistor whenever it is conducting.