Nebulisers for ICP-AES:
As you have learnt in earlier nebuliser is a device that converts a solution of the analyte into finely divided droplets that are carried into the atomiser. You would recall that in concentric type pneumatic nebulisers the sample solution is aspirated through a capillary by the flow of a nebulising gas using Bernoulli's principle and is converted into a fine aerosol through the gas jet. Within a cross flow nebuliser, another type of pneumatic nebuliser, the aspirated sample is nebulised by a stream of argon and the resulting finely separated droplets are carried into the plasma. A schematic diagram of the two types of pneumatic nebulisers used in ICP-AES is given in Figure.
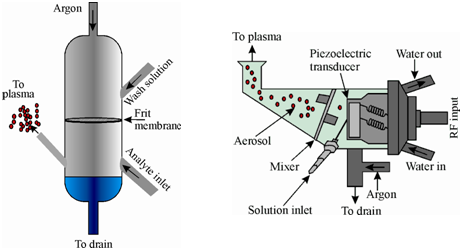
In a frit nebuliser as shown in Figure (a), the sample solution is pumped to a glass frit membrane and consisting of a porous coral such as synthetic material. The argon gas passes through the membrane and converts the sample into an aerosol spray. This is then directed into the plasma. The sample is pumped on to a piezoelectric crystal vibrating at ultrasonic frequencies (50 kHz to 4 MHZ). Vibrations of the crystal break the droplets into smaller particles which are transported to the plasma. Larger aerosol drops are drained out. A schematic diagram of the ultrasonic nebuliser used in ICP-AES is given in Figure (b).
(a) (b)
Figure: (a) Frit nebuliser and (b) ultrasonic nebuliser used in ICP-AES