Jointed Coordinates or Articulated Arm Robots
If the arm can rotate about all three axes, the robot is called a revolute coordinates, articulate or jointed-arm. Figure 19 shows a typical manipulator arm for the articulated robot. Positioning accuracy of this type of robots is approx ± 0.13 mm.
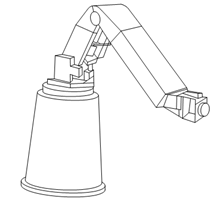
Figure 19 : Typical Motions of an Articulated Robot
Some of the factors to be considered while selecting a robot for integration into a machining cell are :
- Accessibility to the workstation to be tended by the robot - axes of access, clearance/interference distances, doors that open and close, etc.
- Part size, weight and moments of inertia.
- Process speed and time available for part movement, loading, unloading, gaging, etc.
- Part positioning accuracy and repeatability of positioning.
- Variety of tasks and sequences of operations to be performed by the same robot.
- Cell area to be accessed by the robot.
- Complexity of the end effector (gripper) motion necessary to perform the task.
A typical FMC that is tended by two robots is shown in Figure 20. It may be noticed the space relationships between the robots workspace (shown in dashed circular segments around the robots) to the equipment that will be reached by the robot.
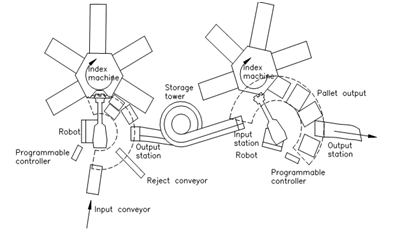
Figure 21: Layout of a FMC Tended by Two Robots