Cartesian Coordinates
Positioning might be done via linear motion along 3 principal axes:
1. Left and right,
2. In and out, and
3. Up and down.
These axes known, correspondingly, as the Cartesian axes X, Y and Z. Figure 17 shows a typical manipulator arm for a Cartesian coordinates robot. The work area or work envelope serviced through the Cartesian-co-ordinates robot's arm is a big box-shaped area. Programming motion for Cartesian-coordinates robot contains specifying to the controller the X, Y and Z values of a wanted point to be reached. After that the robot moves along each axes to the desired point. This is one of the simplest types of robots. Positioning accuracy of this type of robots is approx ± 0.13 mm.
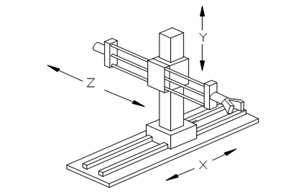
Figure 17: Typical Motions of a Cartesian or Rectilinear Robot