Covalent structure:
Like DNA RNA is a long polymer consisting of nucleotides joined through 3'5' phosphodiester bonds. Moreover, there are some differences:
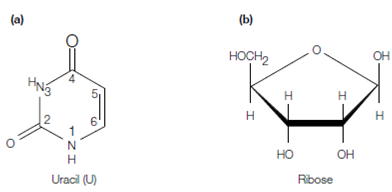
- The bases in RNA are adenine abbreviated A, guanine G, uracil U and cytosine C. therefore thymine in DNA is replaced through uracil in RNA, a several pyrimidine shown in the figure. Moreover, such as thymine, uracil can form base pairs with adenine.
- The sugar in the RNA is ribose rather than deoxyribose as in the DNA.
Equivalent ribonucleosides are guanosine, adenosine, uridine and cytidine. The corresponding ribonucleotides are adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP), guanosine 5'-triphosphate (GTP), cytidine 5'-triphosphate (CTP) and uridine 5'-triphosphate (UTP). As with DNA, the nucleotide sequence of RNA is also written as a base sequence in the 5' → 3' direction. Thus GUCAAGCCGGAC is the sequence of one short RNA molecule.