Efficient market hypothesis:
Eugene Fama introduced the efficient markets hypothesis (EMH) in the finance literature in the mid-1960s. In this theory the word 'market' refers exclusively to financial markets. The basic idea behind this hypothesis is that pricing in efficient financial markets is such that owners of debt and equity securities do not reap any extra-normal returns and benefits. The concept is very similar to that of perfect competition in goods market. Of course, the efficient market hypothesis is based on situations of risk and uses probability theory.
This hypothesis states that because of intense competition in financial markets, pricing of assets would be 'fair'. The efficient market hypothesis postulates that in an efficient market, the current price of an asset reflects all available information about the value of that asset. This means that if we want to draw a trend line, say, of share prices and want to forecast the future price of a share to make some profits, we would gain nothing. The reason is that this theory suggests that others can do the same thing then no one can be persuaded to buy from us so that we gain. In general terms, the EMH suggests that the risk-adjusted expected returns on all investments would be equal. The return that we expect to earn on a particular stock exactly equals the
return that we could earn on any other share with similar risk characteristics. If risk- adjusted returns on all financial assets are equal, we cannot beat the market by picking out a share that we think will do better than other stocks in the market. By chance, we may pick one that does better than average, but the probability of picking one that does worse than average is equally large. That is why the EMH suggests it is better to have a diversified portfolio of assets so that on average we have equal chances of picking a good stock and a bad one.
An important idea behind the EMH is the using of information and forming of expectations about the future value of a variable (in the present case, asset prices).
Before proceeding further, let us first clarify the notion of expectation and expectation formation. We always want to have an idea about the future value of a variable, since there is uncertainty present and we do not have perfect foresight. For instance, we want to know if prices are going to go up, or if there is inflation, whether inflation will persist. For asset prices too, investors are keen to know how asset prices will perform. We look at three ways of expectations formation. : Markov expectations, adaptive expectations and rational expectations. Each method involves a different level of sophistication.
The simplest way to form expectations is the Markov expectations. Put baldly, the Markov expectations suggests the immediate past will continue into the next period. Suppose we denote by Pt the price of an asset at time t; then the expected price of
the asset for time t +1 formed at time t will be Pt . Let us denote by Pe t+1 the expected value of P for time t+1. Then the Markov expectations hypothesis simply states that
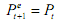
In other words, we simply use the most recent value of P to forecast future values. The most obvious shortcoming of the Markov expectations hypothesis is that it does not take into account knowable events that might change the future environment. if the price is not only rising, but rising at a rising rate each time period, then the Markov expectations hypothesis will not only make systematic error, but the forecast error will rise. However, the Markov expectations hypothesis is a reasonable method of forming expectations at a time when the forecasting environment is stable. If, for instance, there is no inflation, then it might be reasonable to expect that the general price level will stay the same.
The adaptive expectation hypothesis, as the name suggests, says that people form expectations but when forming further expectations, they revise or adapt subsequent expectations in the light of forecast errors that have taken place. Let us try to understand it as follows. Let x be a variable, say the price for a share. Let xet be the expectation about the price of the share that the investor has regarding the current time. Of course this expectation was formed in the last period, at t-1. Suppose 2007 is the current year. In 2006 the investor formed an expectation about share price to prevail in 2007. Let xt be the actual price of the share that prevails in 2007 (of course, prices of shares do not change once a year, and people do not form an expectation once a year, but this is merely for ease of exposition. You can easily think of the previous time as last month, last fortnight, last week or yesterday). Now, the investor has to now make an expectation about the price of the share for next year. So in 2007 the investor makes a forecast about price of the share in 2008. Let xet+1 be the expected price of the share for 2008. The adaptive expectations hypothesis says that that will depend on the forecast error of last time, that is, on . This hypothesis says that (the difference between the expectation for t+1 and that for t) will be influenced by . We can write this formally as
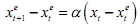
Here α is called the speed of adjustment, and this shows how quickly new expectations adjust to past forecast errors. The above equation can be rewritten as:
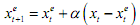
This equation states that the expectation formed now about next period equals the expectation formed in the last time period about the current time period plus a term that a adjusts this old expectation in the light of past forecast.