Transcription and processing of prokaryotic rRNA:
In E. coli there are seven rRNA transcription units scattered by the genome, every of that contains one copy of each of the 16S, 23S and 5S rRNA genes and one to four copies of several tRNA genes which is shown in the diagram. This gene assembly is transcribed through the single prokaryotic RNA polymerase to yield a single 30S pre-rRNA transcript about 6000 nt in the size. This arrangement ensures that stoichiometric amounts of the various rRNAs are synthesized for ribosome assembly. Subsequently transcription, the 30S pre-rRNA molecule forms internal base paired regions to provide a series of stem-loop structures and ribosomal proteins bind to form a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex. The number of the nucleotides in the folded pre-rRNA molecule is now methylated on the ribose moieties by using S-adenosylmethionine as the methyl donor. Subsequently the pre-rRNA fragment is cleaved at specific sites through RNase III to release precursors of the 23S, 16S and 5S rRNAs. The precursors are then trimmed at their 5' and 3' ends through ribonucleases M23, M5 and M16 that will act on the 5S, 16S and 23S precursor rRNAs respectively to generate the mature rRNAs.
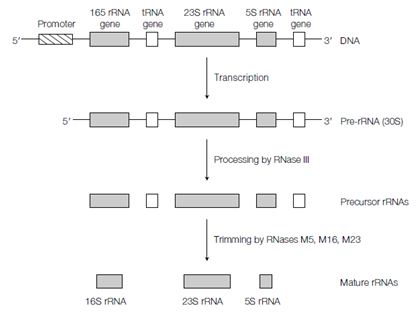
Figure: Transcription and processing of prokaryotic rRNA.
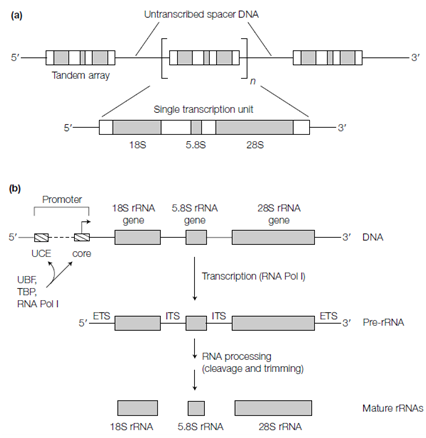
Figure: (a) rRNA transcription units; (b) transcription of a single transcription unit by RNA Pol I and processing of pre-rRNA.