Ribosomes:
Every ribosome consists of two subunits a small subunit and a large subunit, each of that is a multi component complex of rRNAs (ribosomal RNAs) and ribosomal proteins that is shown in the figure. One way of distinguishing among particles like as ribosomes and ribosomal subunits is to place the sample in a tube within a centrifuge rotor and spin this at very high speed. That causes the particles to sediment to the tube bottom. Particles which differ in mass shape anddensity sediment at variant velocities (sedimentation velocities). Therefore a particle with double the mass of another will always sediment faster give both particles have the similar density and shape. The sedimentation velocity of any provided particle is lso straightly proportional to the gravitational forces (the centrifugal field) experienced in during the centrifugation, that can be increased simply through spinning the rotor at a higher speed. Moreover, it is possible to describe a sedimentation coefficient which depends solely on the shape, size and density of the particle and is independent of the centrifugal field. Sedimentation coefficients are commonly measured in Svedberg units (S). The prokaryotic ribosome has a sedimentation coefficient of 70S whereas the small and large subunits have sedimentation coefficients of 30S and 50S; respectively note that S values are not additive. The 50S subunit holds two rRNAs that are 23S and 5S complexed with 34 polypeptides whereas the 30S subunit contains 16S rRNA and 21 polypeptides. In the eukaryotes the ribosomes are larger and harder; the ribosome monomer is 80S and consists of 60S and 40S subunits. The 60S subunit contains three rRNAs (28S, 5.8S and 5S) and about 49 polypeptides and the 40S subunit has 18S rRNA and about 33 polypeptides. Moreover, despite this extra complexity, the whole structure and function of eukaryotic ribosomes is very same to those from bacteria. In every case, about two thirds of the structure is rRNA and one third is protein.
A broad range of studies have establish up a detailed picture of the fine structure of ribosomes, mapping the location of the several RNA and protein elements and their interactions. The whole shape of a 70S ribosome gained by electron microscopy studies is shown in the figure. The 3-D structure of bacterial ribosomal subunits determined only a few years ago described in which the several rRNA are strongly folded and base pair extensively with each other to form the core of the ribosomal subunits with the proteins restricted to the
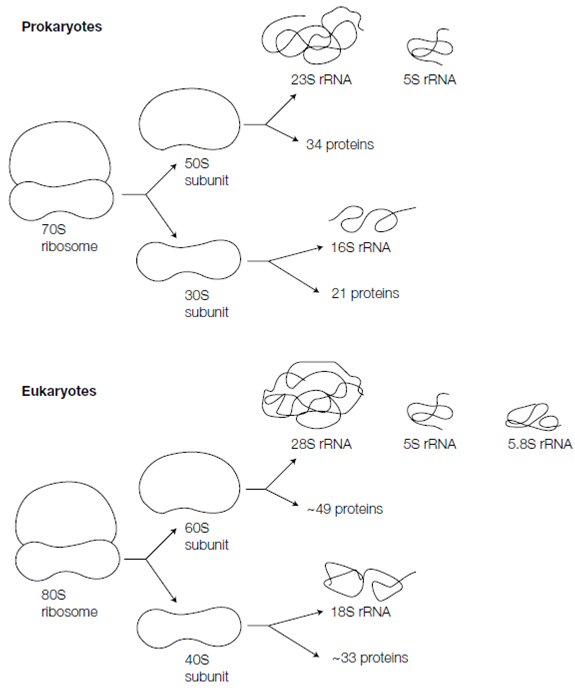
Figure: Composition of ribosomes in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
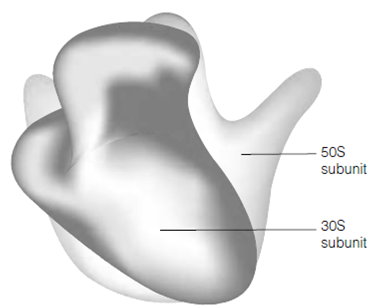
Figure: The prokaryotic 70S ribosome.
surface and filling gaps among RNA folds. Not only are the rRNAs largely responsible for the whole structure of the ribosome but they also form the three major binding sites (the P, A, and E sites) included in protein synthesis. Additionally, the 23S rRNA, rather than a protein forms the catalytic site for peptide bond configuration. Thus, protein synthesis includes rRNAs acting as ribozymes.