Transformed RGB Colour Cube with Interpolated Hues:
Note how the primary colours define unit vectors along the axes. The three corners opposite R, G, and B are cyan (C), magenta (M), and yellow (Y), the basis of the CMY model. The line linking black (0,0,0) and white (1,1,1) is the gray scale line.
Figure illustrates the coordinates and colours of the corners of the RGB colour cube. However, most light may be represented by a 3-D colour vector which terminates at some arbitrary point in the interior of the cube. To understand the additional shadings possible with the colour cube representation, let the shadings possible on the surface of the cube. In Figure, a transformed view of the colour cube is presented in which sub- cubes interpolate the colour between the four corners of the cube.
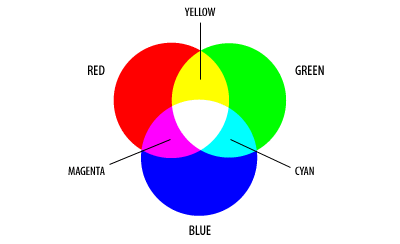
Figure: Transformed RGB Colour Cube with Interpolated Hues