Destabilizing inductive effect:
Finally, we turn to ethanol. The conjugate base is the ethoxide ion that cannot be stabilized through delocalizing the charge, because resonance is not possible. There is no π bond available to participate in resonance. Hence, the negative charge is localized on the oxygen. In addition, the inductive donating effect of the neighboring alkyl group (ethyl) improves the charge and destabilizes it. This creates the ethoxide ion the least stable (or most reactive) of the three anions we have considered. The outcome of that is the ethanol is the weakest acid.
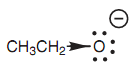
Figure: Destabilizing inductive effect of the ethoxide ion.