Definition of Integral Control:
A device which performs the mathematical function of integration is known an integrator. The mathematical conclusion of integration is known as the integral. The integrator gives a linear output along with a rate of change which is directly associated to the amplitude of the step change input and a constant which specifies the function of integration.
For the instance display in Figure, the step change has amplitude of 10 percent, and the constant of the integrator causes the outcome to change 0.2 percent per second for every 1 percent of the input.
The integrator acts to transform the step change into a gradually changing signal. As you could see, the input amplitude is repeated in the output every 5 seconds. Since long as the input remains constant at 10 percent, the output will continue to ramp up every 5 seconds until the integrator saturates.
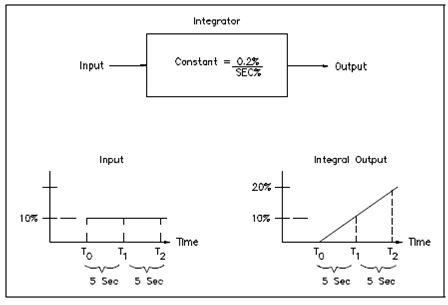
Figure: Integral Outputs for a Fixed Input