Two-point Problem
The back ray method needs drawing the ray from preceding stations (O1 and O2) to the station to be occupied through plane table (say O3). Errors of centering therefore are inevitable.
The two-point problem consists of locating the position of a plane table station on the drawing sheet through observation of two well described points, whose positions have already been plan on plotted. The procedure of resection after orientation through two points is given below.
(a) Let O1 O2 be the two stations plotted as o1 and o2 on the drawing sheet. It is needed to plot station O3 for the plane tabling work.
(b) An auxiliary point A on ground is selected such that AO3 is approximately parallel to O1 O2 and the angle O3 O1 A and O3 O2 A are balanced angles, i.e. these are neither too delicate or too obtuse. The table is set or levelled at A, and so oriented in which line O1 O2 on ground is nearly parallel to line o1 o2 plotted on table map.
(c) Alidade, touching o2 and sighting O2 on ground, a ray is drawn through o2. In the similar way, draw a ray through touching alidade to o1 and sighting O1 on ground. That ray will intersect a first ray at a1 on the map.
(d) With alidade touching a1, sight O3 and draw the ray a1 o3. Mark the approximate position of O3 on the map as o′3.
(e) The table is removed from A and set at O3 with marked position of o3 over O3, properly similarly and levelled oriented. This is achieved through back sighting A from O3.
(f) Now with table at O3, keep alidade touching o1 and sight O1 and draw a back ray resecting the line a1 o′3 in o3. Here o3 is the point representing the station O3 with reference to the approximate orientation made at A.
(g) With alidade touching o3, sight O2 and draw a ray to O2. If the ray passes by the plotted point o2, an orientation of the table is correct and o3 is the right position of O3. While, if this ray cuts the previously plotted line a1 o2 at some other point, say o′2, then the position o3 is not the correct position of O3.
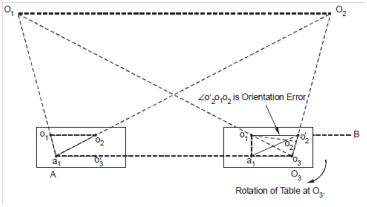
Figure: Two-point Problem
(h) The orientation error will be equal to ∠ o2′ o1 o2 between the lines o1 o2 and o1 o2?. This error could be eliminated through rotating the table through the angle o2? o1 o2. This table rotation can be achieved by taking the following steps.
(i) The alidade is placed along line o1 o2? and a ranging rod B is fixed in line with o1 o2?, far away from the plane table.
(ii) Alidade is now kept along true line o1 o2 and table is rotated so that ranging rod B is bisected. The table is clamped in latest position.
(iii) The true situation of O3 on map is now marked through:
(a) Orienting alidade along o1 O1 and drawing the ray o1 O1, and
(b) Orienting alidade along o2 O2 and drawing the ray o2 O2. The point of intersection of the two rays will provide the correct position of O3 (the new table position) on map.
The new position of table station O3 is, therefore, correctly marked on map along with the help of two previous table stations O1 and O2 already marked on map. The process followed is termed two-point problem within plane table survey.