Parametric Curves:
In parametric form each of the coordinate of a point on a curve is defined as a function of a single parameter. On the curve the position vector of a point is fixed by the value of the parameter. For a two-dimensional curve along t as the parameter, the cartesian coordinates of a point on the curve are following:
x = x (t)
y = y (t)
Then the position vector of a point on the curve is
P (t) = [x (t) y (t)]*
The nonparametric form is attained from the parametric form by removing the parameter to get a single equation in terms of y and x.
The parametric form is appropriate for demonstrating closed and multiple valued curves. The tangent or derivative vector on a parametric curve is provided by:
P′ (t) = [x′ (t) y′ (t)]
Here the ′ denotes differentiation w. r. t. the parameter. The slope of the curve,
dy/dx, is
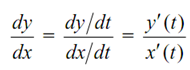
Note down that while x' (t) = 0, the slope is infinite. Therefore an infinite slope is indicated by considering one component of the tangent vector to be zero. Therefore, computational difficulties are ignored using the parametric derivative.