Membrane Lipids
Membrane lipids are a collection of compounds structurally same to oils and fats that form the double-layered surface of all cells. The three main classes of membrane lipids are glycolipids, phospholipids, and cholesterol. Such as membrane, magnets lipids have polarity with one end which is soluble in water polar and an ending which is soluble in fat nonpolar.
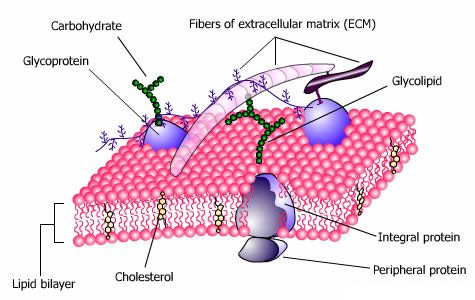
Through forming a double layer with the polar ends pointing outwards and the nonpolar ends pointing inwards membrane lipids can form a lipid bilayer that keeps the watery interior of the cell separate from the watery exterior. The arrangements of lipids and several proteins acting as receptors and channel pores in the membrane control the entry and exit of other molecules as category of the cell's metabolism.