Vapor Compression Refrigeration System
A vapor compression refrigeration system is employed in majority of situations where refrigeration is needed for various purposes. Its popularity is mainly as of its high performance characteristics and problem free working for long time periods.
The figure shown below is the schematic of simple vapor compression refrigeration system (VCRS). This is fundamentally similar as that describes the working of a refrigerator. Here, the working substance, termed as the ‘refrigerant’ endures a thermodynamic cycle whereas transferring heat from the low temperature reservoir (i.e., refrigerated body or region) to the high temperature reservoir (at surroundings) with the help of exterior work.
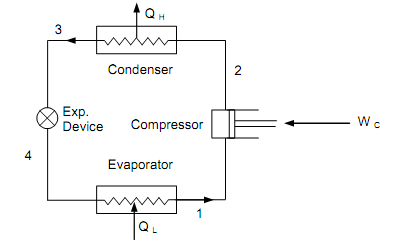
Figure: Schematic of a Simple VCRS
The VCRS, shown in figure above has four main components, viz, EVAPORATOR, COMPRESSOR, CONDENSER and EXPANSION DEVICE. The ideal or the fundamental cycle on which such a system functions is shown in figure below on both T–s and p–h diagrams.
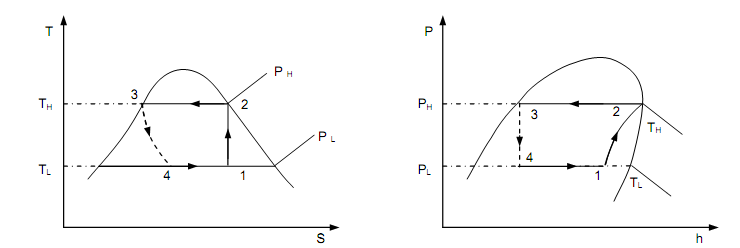
Figure: VCR Cycle (i.e., Wet Compression)
The wet refrigerant vapor at state 1 from the evaporator comes in the compressor. This vapor is compressed reversibly and adiabatically to saturated vapor at state 2. Suppose the work needed by the compressor be W. At state 2 the pressure is equivalent to the saturation pressure of the refrigerant analogous to the condenser temperature. The high pressure vapor at state 2 is condensed to saturated liquid at similar pressure as it passes via the condenser and assumes QH be the heat transferred from the refrigerant to the surrounds at TH. The saturated liquid at state 3 is then throttled via the expansion machine to low quality vapor at state 4. At state 4 the pressure of the refrigerant vapor communicates to its saturation pressure at the evaporator temperature. This low quality vapor, as it flows via the evaporator, picks up heat to sustain the refrigerated space at a temperature TL, and then quits it at state 1 as high quality vapor. Assume QL be heat transferred to the refrigerant at the evaporator.