Performance of Vapor Compression Refrigeration System
The performance of a VCRS is stated, by its Coefficient of Performance (COP).

Applying the First Law to the cycle,
W = QH - QL
and therefore,
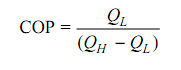
The relations below who give the magnitudes of heat and work communications might be acquired by the application of SFEE (depend on unit mass) to the four components of the VCRS. The state points marked on schematic (figure is as shown below) and the cycle diagram (the figure is as follows), are well-suited.
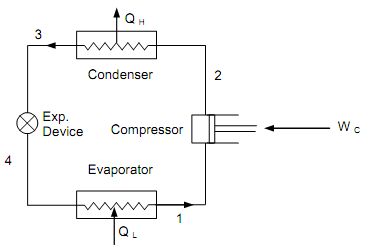
Figure: Schematic of a Simple VCRS
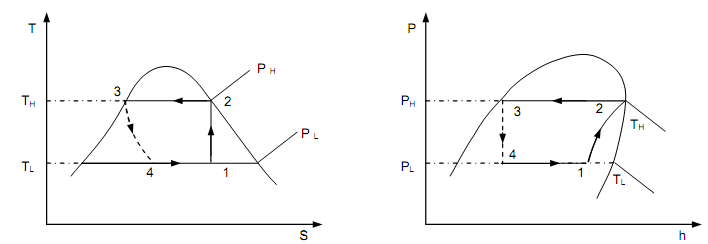
Figure: VCR Cycle (Wet Compression)
QL = h1 – h4
W = h2 – h1
h3 = h4
Using all the above equations it might be further written that:
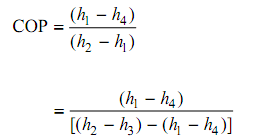
Refrigerating Effect:
In refrigeration technology, the cooling generated per kg refrigerant is termed to as the refrigerating effect. As a result,
Ref. effect = (h1 – h4) kJ/kg
Capacity of the VCRS:
The capacity of a VCRS, stated in kW, is the rate at which cooling is generated in the evaporator, As a result,
Capacity = (Mass flow rate of the refrigerant) × (Ref. effect)
i.e.,
Capacity = m x (h1 – h4) KW
Here m is in kg/s and h is in kJ/kg.
Ton of Refrigeration:
This is the unit of capacity of the refrigeration system generally used in British System of Units. The refrigeration system is thought to have a capacity of one ton when it can give cooling at a rate of 200 BTU/min. This is so since a system cooling at this rate can entirely freeze one ton (2000 lbs) of water at 32oF to ice at similar temperature in a day (i.e., 24 hours). This can simply be checked by supposing the enthalpy of fusion of water to be 144 BTU/lb.
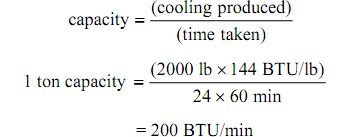
Since of its long time constant use in the refrigeration industry, such unit of capacity has come to remain and is employed broadly everywhere irrespective of the system of units employed. It is recommended not to use this unit of capacity in SI system of Units. Here the capacity is best represented in kW. Though, to have a feel for the relative magnitudes of ‘1 ton’ and ‘1 kW’ the conversion below factor can be employed.
1 ton = 200 BTU/min = 3.5 kW.
Compressor Power:
This is the power to be supplied to the system from surroundings.
Power = (mass flow rate of refrigerant) × (work per kg)
That is, P = m x (h2 – h1) KW
Here m is in kg/s and h is in kJ/kg.