Working pressure of condenser and evaporator:
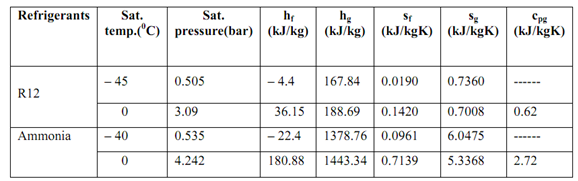
A refrigerator is to be designed to operate among 228 K (- 45 0C) & 273 K (0 0C). The choice is to be made out of the refrigerants: R12 & ammonia. From the data provided in the table below, compute the following:
1) COP, 2) power per ton, 3) compression ratio, 4) working pressure of condenser and evaporator and 5) compression temperature.
Solution:
Considering to the T-s diagram given below in figure
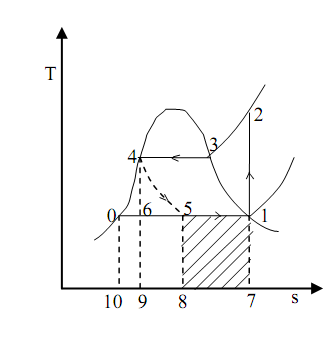
T-S Diagram of the Problem
R12 (dichlorodifluoromethane)
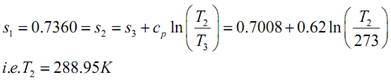
Then,
h2 = h3 + c p (T2 - T 3 )= 188.69 + 0.62(288.95 - 273)
i.e. h2= 198.58 kJ kg
(a)
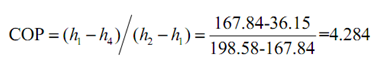
(b) Power per ton is given by: 3.5 /COP = 0.8169kW
R717 (Ammonia)
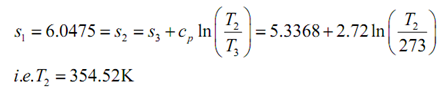
Then,
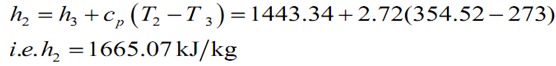
h2 = h3 + c p (T2 -T 3 ) =1443.34 + 2.72(354.52 -273)
i.e. h2 = 1665.07 kJ kg
(a) 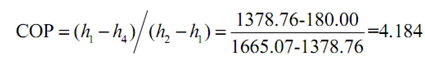
(b) Power per ton is given by: 3.5 /COP = 0.8365kW
The table of the comparison of the above refrigerants is shown below:
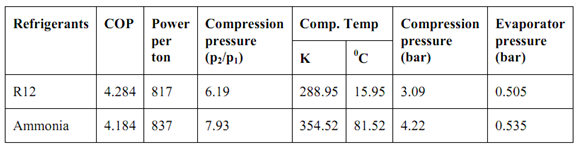
From the described tabular values, we might see that from the sight of power consumption, R12 is better than ammonia. Through, it gives negative evaporator pressure that is less than the atmospheric pressure. Ammonia, too suffers from the similar problem. We may also see that the difference in COP & power consumption of ammonia & R12 is not very much. But, as ammonia is toxic, its use is very limited. R12 is broadly used in home refrigeration systems. The difficulty of negative evaporator pressures is conquering by employing a hermetically sealed compressor that prevents the leakage of air into the evaporator.