Dissolving metal reduction:
An alkyne's reduction to an E-alkene can be acquired if the alkyne is treated with lithium or sodium metals in ammonia at lower temperatures. This is termed as a dissolving metal reduction.
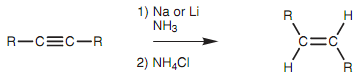
Figure: Reduction of an alkyne to an E-alkene
Within this reaction, the alkali metal donates its valence electron to the alkyne to generate a radical anion. This in turn removes a proton from ammonia to generate a vinylic radical that receives an electron from a second alkali metal to generate a trans-vinylic anion. This anion then removes a proton from a second molecule of ammonia and generates the Tran- or E-alkene. Note: half curly arrows are employed in the mechanism because this is a radical reaction involving the movement of single electrons.
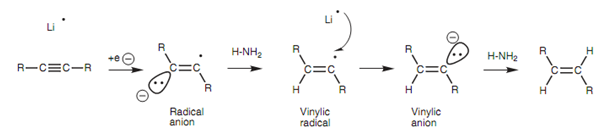
Figure: Mechanism for the dissolving metal reduction of an alkyne.