Graph of potential energy versus reaction coordinate:
The catalyst is crucial because the reaction will not occur at room temperature in its nonexistence. This is since hydrogenation has a high free energy of activation (ΔG1*). The role of the catalyst is to bind the alkene and the hydrogen to a common surface like that they can react much more easily.
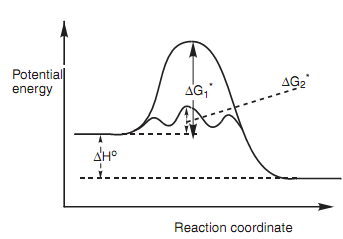
Figure: Graph of potential energy versus reaction coordinate for an uncatalyzed and a catalyzed hydrogenation reaction of an alkene.
This results in a much lower energy of activation (ΔG2*) permitting the reaction to proceed within much milder conditions. The catalyst itself is not changed after the reaction and can be employed in small quantity.
Both of the hydrogen and the alkene are bound to the catalyst surface before the hydrogen atoms are transferred the meaning of this is that both hydrogens are added to similar side of the double bond - syn-addition.
Note: The hydrogen molecule is split one time it has been added to the catalyst.

Figure: Binding of alkene and hydrogen to catalytic surface.