Process of Human Resource Planning
The procedure of HRP usually followed in a big organisation, consists of the steps described below:
Forecasting the Demand for Human Resources
Most of the firms estimate how many employees they needs in future. The demand for human ability at several levels is primarily due to the factors described following:
1. External challenges: These challenges occur from three important sources:
- Economic developments: Liberalisation, opening of banking sector, capital market reforms, the on-line trading systems has created vast demand for finance professionals during the time 1990-1995 in India. The late 90s saw the increase of manufacturing, FMCG, Auto-components, Pharmaceuticals, Healthcare and Chemical Industries in a stable manner. As a result, the demand for Engineering, Scientists and Healthcare professionals and Management graduates has picked up in current times.
- Political, social, legal and technical changes: The demand for definite categories of employees and skills is also affected by changes in legal, political and social structure in an economy. Similarly, firms employing latest technology in, power, automobiles, construction, software, etc., have significantly enhanced the worth of technicians and engineers throughout the last couple of years. However, technology is a double-edged weapon and therefore, its impact on HR plans is not easy to predict. For instance, computerisation programme in, Railways, Banks, Post and Telegraph Departments may dropped demand in one department ( for instance book keeping) while developing it in another (like computer operations). High technology with all its assistant benefits may compel organisations to go lean & downsize workforce suddenly. Employment planning under such circumstance becomes complexes.
- Competition: In fields Companies operating where a big number of players are bent upon cutting each other's throat (having a view to enhance their market shares) frequently reduce their workforce. Competition is helpful to customers but suicidal for companies operating on thin margins. Such kind of companies has to essentially go 'lean' by dropping their workforce. In contrast, companies that are performing well and smoothly progressing will always look for people with crucial skills.
2. Organisational decisions: The organisation's tactical plan, sales and manufacture forecasts and new ventures ought to all be taken into account in employment planning. If Britannia Industries Ltd expects superior demand for biscuits and bread, the long- term HR plan have to take this into consideration. The same, if it tries to venture into other lucrative fields like as milk based products and sweet items, the require for people possessing requisite skills in those areas in the next couple of years might be looked into carefully.
3. Workforce factors: Demand is changed by, terminations, retirements, resignations, deaths and leaves of absence. However, Past experience makes the rate of occurrence of these actions by employees quite predictable.
4. Forecasting techniques: Commonly the manpower forecasting techniques employed by modern organisations are described below:
- Expert forecasts: In this method, managers approximate future human resource requirements, by using their experiences and judgements to good effect.
- Trend analysis: HR needs may be estimated by examining past trends. Past rates of change may be projected into the future or employment growth may be estimated by its relationship with a specific index.
Box 1: Trend Analysis (An Example)
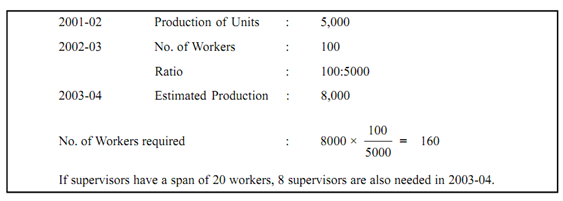
If supervisors have a span of 8 supervisors, 20 workers, are also required in 2003-04.
5. Other methods: Various mathematical models, with the aid of computers are also utilized to forecast HR needs, for example: optimisation models, regression, budget and planning analysis.
To systematically proceed, human resource professionals generally follow three steps. Let's check up these steps as applied in reference of a commercial bank.
- Workforce analysis: The average loss of manpower due to reason of leave, transfer, death discharge, and retirement etc., during the last 5 years can be taken into account. The charge of absenteeism and labour turnover might also be taken into account. The behaviour of competition say from foreign banks, another non- banking financial institution can also be considered here to discover actual requirements in a year (Box. 2).
Box 2: Manpower Flows in a Bank
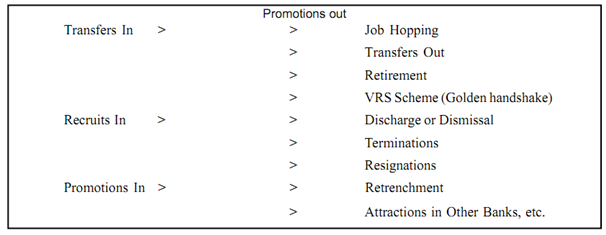
When some of the external and interchanges supply could be predicted (growth opportunities, transfers, promotions, retirements, etc.) others are not so simple to predict. Past experience and historical data can help bank managers in this regard.
- Work load analysis: The requirement for manpower is also determined on the basis of work-load analysis, wherein the company attempt to calculate the total number of person's necessary for various jobs with reference to a planned output - after providing weight age to factors like absenteeism, idle time, etc. The following instance would throw light on this:
Box 3: Work Load Analysis (An Example)
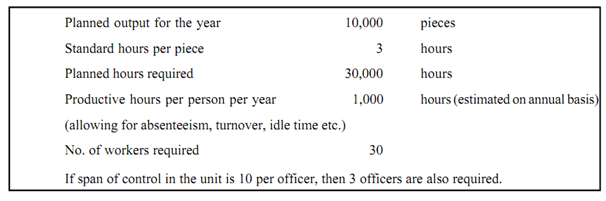
When determining manpower requirements by work load analysis, commercial banks may must take the factors into consideration which are following: (i) the overall number of transactions to be handled by an employee; (ii) the entire amount of deposits and advances per employee; (iii) special requirement in respect of, currency chests, mobile branches, managing extension, counters etc.; (iv) future development plans of the bank concerned. Managerial judgement - a study of the ancient times trends - may serve as a useful guide in this regard. Statistical and econometric models may also be pressed into service, sometimes, depend on the requirement(s).
- Job analysis: Job analysis helps in discovering the abilities or skills needed to do the jobs efficiently. Usually a detailed study of jobs is made to recognize the qualifications and experience compulsory for them. Job analysis includes two things: job specification and Job description. Job specification gives information on the human attributes in terms of, skills, education, aptitudes and experience required to perform a job effectively. Job description is a realistic statement of the duties and responsibilities of a particular job. It provides an indication of how it is to be done , what is to be done, and why it is to be done