Efficiency Of A Compressor
The efficiency of a compressor working in a stable flow process might be defined as
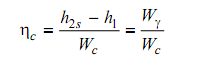
Here:
Wc = Shaft work supplied to the real compressor per kg of gas passing through.
Wγ = Shaft work supplied to a reversible adiabatic compressor per kg of gas compressed from similar initial state to similar final pressure as in the real compressor.
The above efficiency is commonly termed to as the adiabatic efficiency
When the desirable idealized procedure is taken to be the reversible isothermal process, then the compressor efficiency is termed as the isothermal efficiency
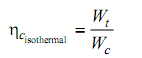
Here:
Wt = Shaft work supplied to the reversible isothermal compressor for compressing 1 kg gas from the similar initial state to the real final pressure.
The common thermodynamic practice is to use the reversible adiabatic basis. Since of the effects of cooling, the adiabatic efficiency of an actual compressor might be greater than unity.
Most of the turbine-type compressors are necessarily adiabatic machines and for such machines the work of compression,
Wc = h2 – h1
Then for adiabatic compressor the efficiency is,
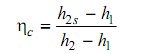
As against this, the original equation provides the adiabatic efficiency of any machine.