Interest:
The major interest of any chromatographer is good separation or resolution between neighbouring peaks. That helps in accurate qualitative analysis and quantitative determination of solutes being divided from a mixture. The resolution of chromatographic peaks is associated to the following two factors:
1. Column efficiency
2. Separation factor (Solvent efficiency)
The column efficiency is concerned with the peak broadening of an initially compact band as it passes through the column. The broadening concludes from the column design and operating conditions. This can be quantitatively described by the plate height (H), which is that length of the column necessary for the attainment of solute equilibrium between the moving gas phase and the stationary liquid phase. The separation factor, (α), on the other hand, results from the solute-solvent (liquid phase) interaction and determines the relative position of solute peaks on a chromatogram. The separation factors or associative retention is expressed as the ratio of retention times. Therefore α is determined through the respective distribution constants (Kc) of the solutes in the liquid phase at a given temperature. The idea of increased column and solvent efficiency is illustrated in Figure.
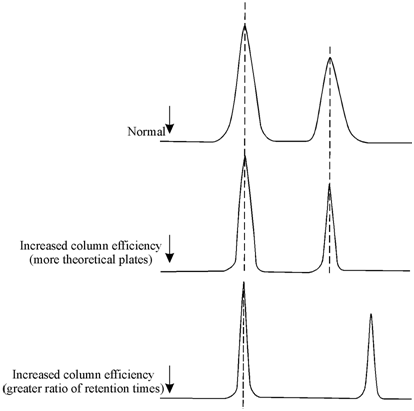
Figure: Illustration of column and solvent efficiency