Column Efficiency:
Column .efficiency is measured through the plate number, N. To compare column efficiency here one must specify the liquid stationary phase, solute (s), temperature, flow rate of carrier gas and sample size. As begin from the Unit 4, the plate concept is a carryover from distillation procedure whereas historically, the first capable columns were in fact composed of discrete plates. In the laboratory, however, packed distillation columns are more commonly employed and the plate number is a theoretical concept introduced so that column performance can be evaluated.
Within Gas Chromatography, as in distillation, a discrete plate is an artificial concept. The plate number acquired in the techniques varies greatly and should not be taken as a direct measure of the difference in their separating power. Plate number is meaningful to compare same columns, or set standards for packing techniques. The plate number could be simply measured from the chromatograms. Figure shows the measurements needed to make this calculation.
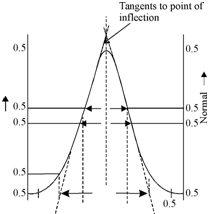
Figure: A normal distribution curve. The inflection point at 0.607 of the peak height. The quantity wb is the width at 0.005 of the peak height (half-height) and corresponds to 2.354 σ. The quantity wb is the base width and corresponds to 4σ as indicated.
N = ( t R/ σ ) 2 = 16( t R /Wb ) 2 = 5.54( t R/Wb ) 2