Nucleophilic substitutions of an ester:
Hydrochloric acid is released in these reactions and this might lead to side reactions. As a result, pyridine or sodium hydroxide might be added in order to mop up the hydrochloric acid shown in figure.
The Acid anhydrides can be transformed to esters and amides however not to acid chlorides.
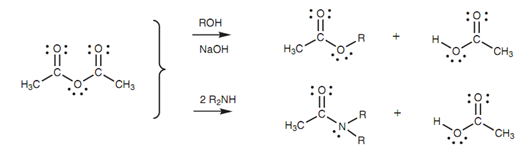
Figure: Nucleophilic substitutions of acid anhydrides.
Esters can be transformed to amides although not to the acid anhydrides or acid chlorides.

Figure: Nucleophilic substitutions of an ester.
Esters can as well be transformed by nucleophilic substitution from one type of ester to other - a process termed as transesteri?cation. For instance, a methyl ester could be dissolved in ethanol in the existence of an acid catalyst and transformed to an ethyl ester. The reaction is an equilibrium reaction, however if the alcohol to be introduced is employed like solvent, it is in large excess and the equilibrium is shifted to the preferred ester. Additionally, if the alcohol to be replaced has a low boiling point, it can be distilled from the reaction since it is substituted, so shifting the equilibrium to the desired product.
Amides are the least reactive of the acid derivatives and cannot be transformed to acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, or esters.