Hydrolysis:
Reactive acid derivatives (that is acid chlorides and acid anhydrides) are hydrolyzed through water to provide the constituent carboxylic acids. The reaction is other example of nucleophilic substitution in which water works as the nucleophile. Hydrochloric acid is a byproduct from the hydrolysis of an acid chloride, thus pyridine is frequently added to the reaction mixture to mop it up.
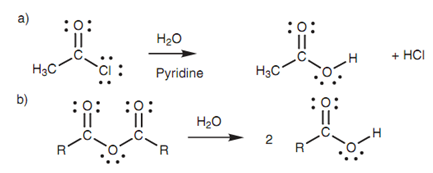
Figure: Hydrolysis of (a) an acid chloride; (b) an acid anhydride.
Esters and amides are much less reactive and thus the hydrolysis needs more forcing conditions by using aqueous sodium hydroxide or aqueous acid with heating.