Resonance effect of a para-nitro group on a phenol:
The kind of substituents present on the aromatic ring can have a profound influence on the acidity of the phenol. This is since substituents can either stabilize or destabilize the partial negative charge on the ring. As better the partial charge is stabilized, as much more effective the resonance will be and the more acidic the phenol will be. Electron-withdrawing groups like a nitro substituent increase the acidity of the phenol because they stabilize the negative charge via an inductive effect. Nitro groups that are ortho or para to the phenolic group have an even greater influence. This is since a fourth resonance structure is possible that delocalizes the partial charge even further. Electron-donating substituents (for example alkyl groups) have the opposite effect and decrease the acidity of phenols.
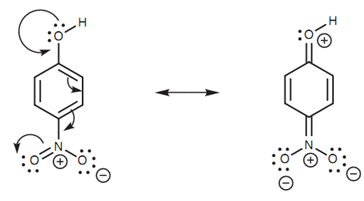
Figure: Resonance effect of a para-nitro group on a phenol.