Crossed Aldol reaction:
Till now we have talked about the Aldol reaction being employed to link two molecules of similar aldehyde or ketone, although it is also possible to link two dissimilar carbonyl compounds. This is termed as a crossed Aldol reaction. For instance, benzaldehyde and ethanal can be connected in the existence of sodium hydroxide.
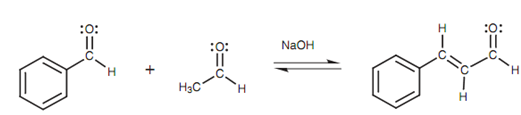
Figure: Crossed Aldol reaction
In this instance, ethanal reacts along with sodium hydroxide to form the enolate ion that then reacts with benzaldehyde. Elimination of water takes place easily to give an extended conjugated system including the aromatic ring, the double bond, and the carbonyl group.
This reaction acts well since the benzaldehyde has no α-protons and cannot make an enolate ion. Hence, there is no possibility of benzaldehyde undergoing self-condensation. It can only work as the electrophile for another enolate ion. Though, what is to stop the ethanal going through an aldol addition with itself?