Diazonium salts:
Primary arylamines or anilines can be transformed to diazonium salts that in turn can be converted to a large range of substituents.
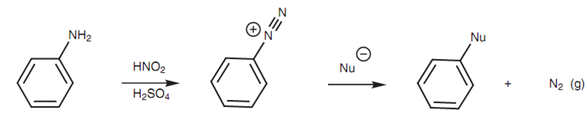
Figure: Synthesis and reactions of diazonium salts
Reaction of an aniline along with nitrous acid results in the formation of the stable diazonium salt in a process termed as diazotization. In the strong acid conditions employed, the nitrous acid dissociates to make a +NO ion that can then act like an electrophile.

Figure: Mechanism of diazotization
The aromatic amine employs its lone pair of electrons to make a bond to this +NO ion. Loss of a proton from the intermediate formed, followed through a proton shift directs to the formation of a diazohydroxide. Now the hydroxide group is protonated turning it into a good leaving group, and a lone pair from the aryl nitrogen makes a second π bond among the two nitrogen atoms and expels water.