Elimination
Alcohols, such as alkyl halides, can go through elimination reactions to form alkenes. Because water is eliminated, the reaction is also termed as dehydration.
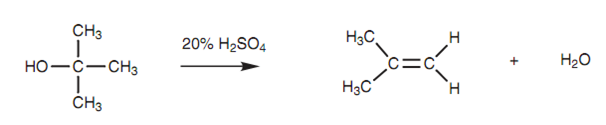
Figure: Elimination of an alcohol.
Like alkyl halides, the elimination reaction of an alcohol needs the existence of a susceptible proton at the β-position.

Figure: Susceptible β-protons in an alkyl halide and an alcohol.
While the elimination of alkyl halides is performed under basic conditions, the elimination of alcohols is performed under acid conditions. Within basic conditions, E2 elimination would need the loss of a hydroxide ion as a leaving group. Because the hydroxide ion is a strong base, it is not a good leaving group and thus the elimination of alcohols within basic conditions is hard to achieve.