Eddy Diffusion Term (A):
This factor arises from the multiplicity of pathways for a gas flowing by the column; thus, it is also known as 'multiple flow paths' term. The column is packed with particles of various sizes and shapes arranged in an irregular manner. As the carrier gas flows through the channels of the packing, it is divided into many streams, some of which may merge and again divide in a complex manner. Thus, the molecules travel through a series of tortuous pathways. The solute molecules carried by the gas will face a same fate. They will follow several paths, some shorter, some longer than the average distance. The condition is described by taking the example of two molecules passing through the column.
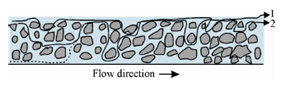
Figure: Typical pathways of two molecules 1 and 2, 2 will travel longer distance than 1
This will mean that the original solute plug will spread out. Some molecules will reach the detector sooner, a few later and several at the average time. The magnitude of contribution of eddy diffusion has to depend on the size, shape and uniformity of packing particles.