Instrumentation for Raman Spectroscopy:
There are two main issues in Raman spectroscopy that need to be addressed by suitable instrumentation. First one is the inherent weakness of the Raman scattering signal as compared to the intense Rayleigh scattering and the second is about the spectral resolution that is the ability to resolve features inside the spectrum. Like the IR instruments, there are five basic components of a Raman spectrometer. These are given below:
- An intense laser source
- Sample handling unit
- Monochromator or interferometer
- Detector
- Signal processing and output device
A schematic representation of the common set up of the monochromator based dispersion Raman spectrometer is given in Figure and that of the interferometer based FT-Raman spectrometer is given in Figure.
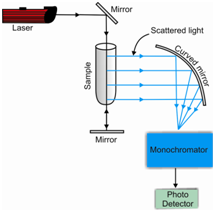
Figure: Schematic representation of the experimental set up of a dispersion Raman spectrometer
You might search the arrangements to be same to that of the corresponding IR instruments along with the only difference being that the scattered radiation is collected at right angles to the radiation and it is passed by a filter before sending to a transducer for detection. A Raman spectrometers differ from the IR instruments in terms of the sources, a sample handling devices and the transducers used for detecting the scattered radiation.