Tropospheric EM propagation
At the frequencies above around 30 MHz, the lower atmosphere bends radio waves towards surface. Tropospheric banding or tropo occurs as the index of refraction of air, with respect to EM waves, decreases with the altitude. The effect is similar to sound waves hugging surface of a lake in early morning, letting you hear the conversation a mile away. Tropo makes it possible to communicate for hundreds of miles when ionosphere will not return waves to the earth.
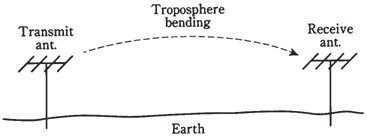
Figure--The low=-987654er atmosphere bends EM waves toward surface.
Another type of tropospheric propagation is called as ducting. It occurs when EM waves are trapped in layer of cool, dense air sandwiched between 2 layers of warmer air. Like ducting, bending,occurs entirely at frequencies over 30 MHz.The other tropospheric propagation mode is troposcatter. This takes place as the dust grains, air molecules, and water droplets scatter some EM field at very high and ultra high frequencies (over 30 MHz).