Elastic scattering:
Elastic scattering is the most likely interaction among fast neutrons and low atomic mass number absorbers. An interaction is sometimes referred to as the "billiard ball effect." A neutron shares their kinetic energy along with the goal nucleus without exciting the nucleus.
Radiative capture (n, γ) takes place while a neutron is absorbed to generate an excited nucleus. An excited nucleus regains stability through emitting a gamma ray.
The fission process for uranium (U238 or U235) is a nuclear reaction whereby a neutron is absorbed through the uranium nucleus to form the mediater (compound) uranium nucleus (U239 or U236). Compound nucleus fissions within two nuclei (fission fragments) along with the concurrently emission of one to various neutrons. The fission fragments generate have a combined kinetic energy of about 168 MeV for U235 and 200 MeV for U238 that is dissipated, causing ionization. The fission reaction could occur along with either fast or thermal neutrons.
The distance in which a fast neutron will travel, among its introduction into the slowing-down medium (moderator) and thermalization, is dependent on the number of collisions and the distance among collisions. By the real path of the neutron slowing down is tortuous since of collisions, the average straight-line distance could be determined; this distance is known as the fast diffusion length or slowing-down length. A distance traveled, at once thermalized, until the neutron is absorbed, is known as the thermal diffusion length.
Fast neutrons rapidly degrade in energy through elastic collisions while they interact along with low atomic number materials. Since neutrons reach thermal energy, or close thermal energies, the likelihood of capture increases. Within present day reactor facilities the thermalized neutron continues to scatter elastically along with the moderator until it is absorbed through fuel or non-fuel material or until that leaks from the core.
Secondary ionization caused by the capture of neutrons is important in the detection of neutrons. A Neutron will interact with B-10 to generate Li-7 and He-4.
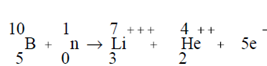
The alpha and lithium particles share the energy and produce "secondary ionizations" those are simply detectable.