Alpha Particle:
The alpha particle is a helium nucleus generates from the radioactive decay of heavy metals and a few nuclear reactions. Alpha decay often occurs between nuclei which have a favorable neutron/proton ratio, but contain too several nucleons for stability. An alpha particle is a massive particle consisting of an assembly of two protons and two neutrons and a resultant charge of +2.
Alpha particles are the least penetrating radiation. The main energy loss for alpha particles is due to electrical excitation and ionization. Since an alpha particle passes by air or soft tissue, it loses, on the average, 35 eV per ion pair created. Because of its large mass, highly charged state, and low velocity, the specific ionization of an alpha particle is extremely high.
Below Figure describes the specific ionization of an alpha particle, on the sequence of tens of thousands of ion pairs per centimeter in air. An alpha particle travels a associatively straight path over a short distance.
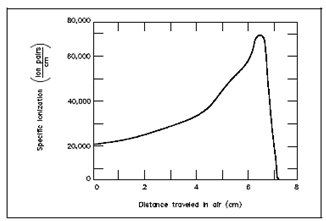
Figure: Alpha Particle Specific Ionization -vs- Distance Traveled in Air